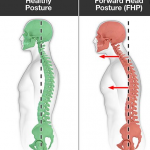
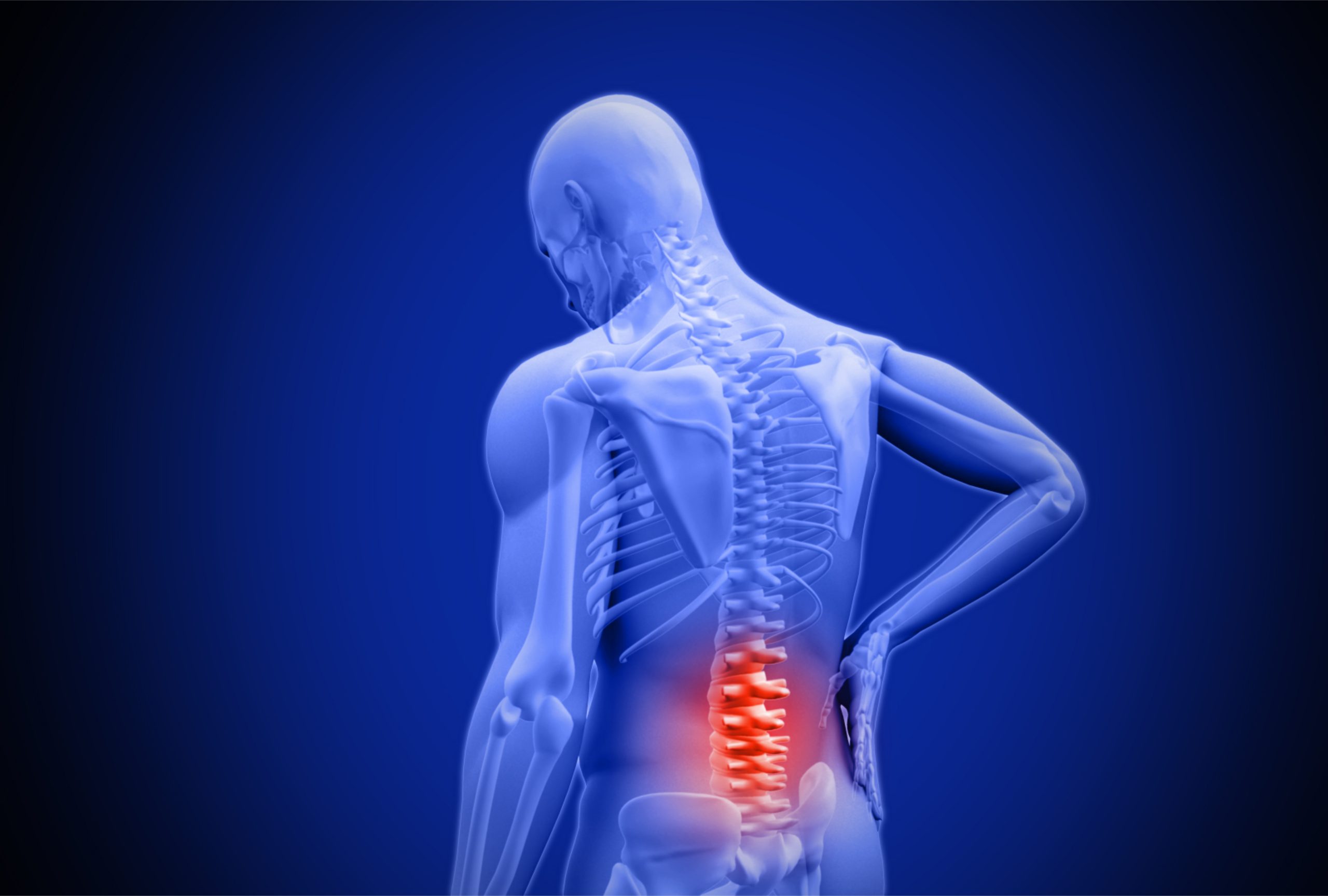
Scoliosis is a condition that affects the spine, causing it to curve to one side. It can occur in people of all ages, but it is most commonly diagnosed during adolescence. The curvature of the spine can cause lower back pain and discomfort, and in severe cases, it can lead to mobility issues and affect a person’s quality of life.
Structural or functional Scoliosis

Structural scoliosis is caused by a permanent deformity in the spine, such as a congenital defect or a result of another condition like muscular dystrophy or cerebral palsy.
Non-structural scoliosis, also known as functional scoliosis, occurs when the spine develops a temporary curve due to factors like muscle imbalances, leg length discrepancies, or poor posture.
Back pain with Scoliosis
Back pain is a common symptom associated with scoliosis. The severity of the pain can vary depending on the degree of the spinal curvature, the age of the individual, and other factors. Some people with scoliosis may experience mild discomfort, while others may have more severe pain that can limit their mobility and daily activities.
Causes of Scoliosis
The exact cause of scoliosis is not known, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the risk factors for developing scoliosis include a family history of the condition, certain medical conditions such as cerebral palsy and muscular dystrophy, and abnormalities in the spinal cord.
One of the most common symptoms of scoliosis is lower back pain. This pain can be dull or sharp and is often exacerbated by standing or sitting for prolonged periods of time. Other symptoms of scoliosis include uneven shoulders or hips, a visible curvature of the spine, and muscle spasms or stiffness.
Treatment options for Scoliosis
 Treatment for scoliosis depends on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, regular monitoring and physical therapy may be sufficient to manage symptoms and prevent the curvature from worsening. In more severe cases, bracing or surgery may be necessary to correct the curvature of the spine.
Treatment for scoliosis depends on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, regular monitoring and physical therapy may be sufficient to manage symptoms and prevent the curvature from worsening. In more severe cases, bracing or surgery may be necessary to correct the curvature of the spine.
Physical therapy is often recommended for patients with scoliosis as it can help to improve flexibility, reduce pain, and prevent further curvature of the spine.
Exercises that target the core and back muscles are particularly beneficial for those with scoliosis, as they can help to improve posture and alignment.
Bracing is also commonly used to treat scoliosis, especially in children and adolescents whose bones are still growing. A brace is a specialized device that is worn around the torso to help prevent further curvature of the spine.
The type of brace used depends on the location and severity of the curvature, as well as the patient’s age and activity level. In severe cases of scoliosis, surgery may be necessary to correct the curvature of the spine. The most common surgical procedure for scoliosis is spinal fusion, which involves fusing together two or more vertebrae to create a single bone. This helps to stabilize the spine and prevent further curvature.
FAQ’s
- What is scoliosis? Scoliosis is a medical condition in which the spine curves sideways instead of being straight. This condition affects the shape and structure of the spine, causing it to bend and twist into an abnormal position.
- What causes scoliosis? The exact cause of scoliosis is still unknown, but it can be attributed to a number of factors. Some of the most common causes include genetic factors, neuromuscular conditions, and developmental disorders.
- What are the symptoms of scoliosis? The symptoms of scoliosis can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Some common symptoms include uneven shoulders or hips, a visible curvature of the spine, back pain, and fatigue.
- How is scoliosis diagnosed? Scoliosis can be diagnosed through a physical examination and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans. During a physical exam, your doctor will look for signs of scoliosis such as uneven shoulders or hips, or a visible curvature of the spine.
- Can scoliosis be treated? Yes, there are a number of treatments available for scoliosis. The most common treatments include bracing, physical therapy, and surgery. The best course of treatment will depend on the severity of the condition and the age of the patient.
- Can scoliosis cause complications? In some cases, scoliosis can cause complications such as breathing difficulties or chronic pain. Severe cases of scoliosis can also cause the spine to twist and compress the internal organs, which can lead to further health problems.
- Is scoliosis preventable? There is no surefire way to prevent scoliosis, but maintaining good posture and engaging in regular exercise can help strengthen the muscles that support the spine. It is also important to seek treatment as soon as possible if scoliosis is detected, as early intervention can prevent the condition from worsening.
Managing Scoliosis
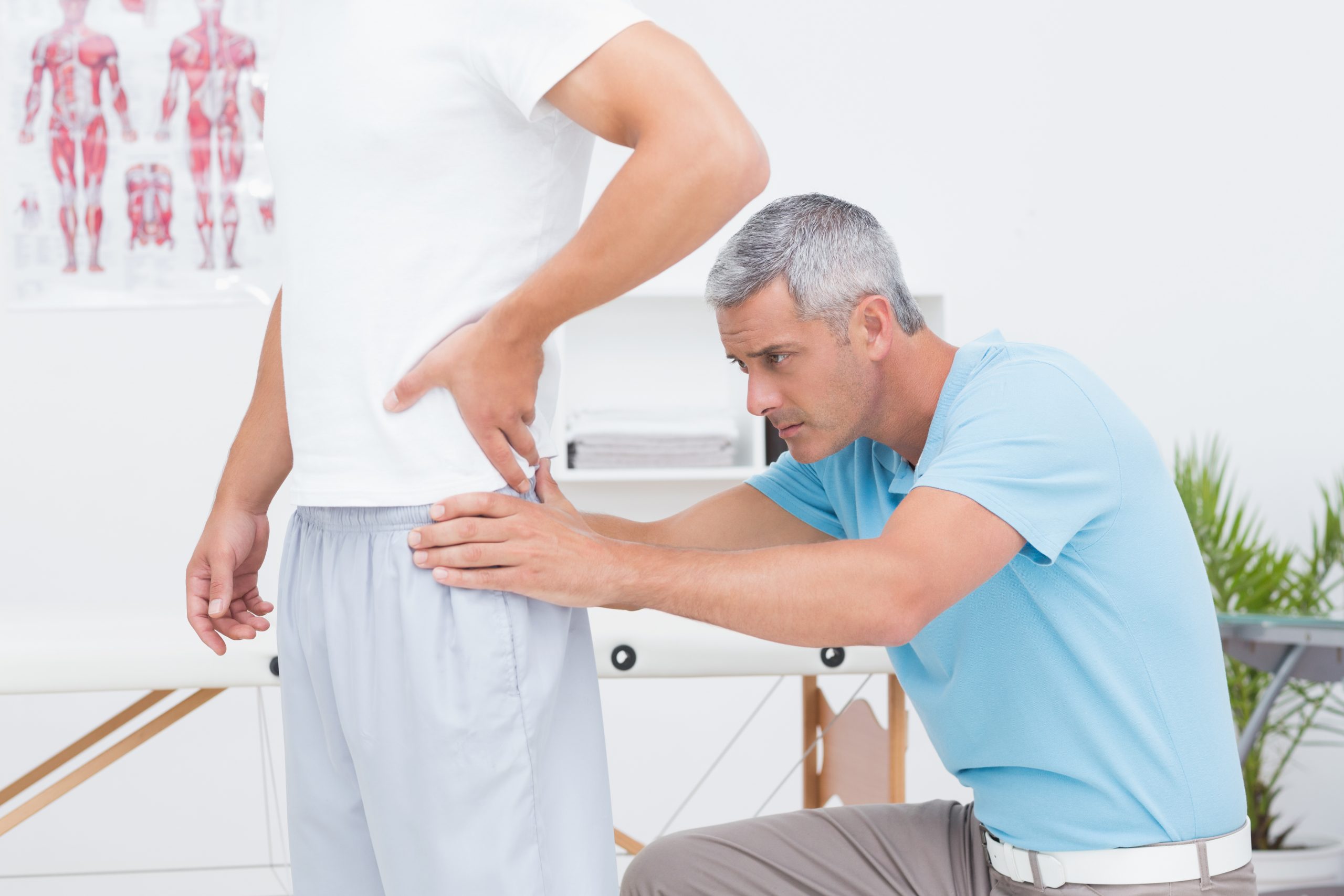
While scoliosis can be a challenging condition to manage, there are many effective treatment options available.
By working closely with a healthcare provider and following a personalised treatment plan, patients with scoliosis can effectively manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of scoliosis, it is important to seek a healthcare professional to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. It’s important for individuals with scoliosis to work closely with their healthcare providers, including orthopedic specialists, to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on their specific condition.
Regular monitoring and early intervention can help manage scoliosis effectively and improve the overall well-being of the individual.