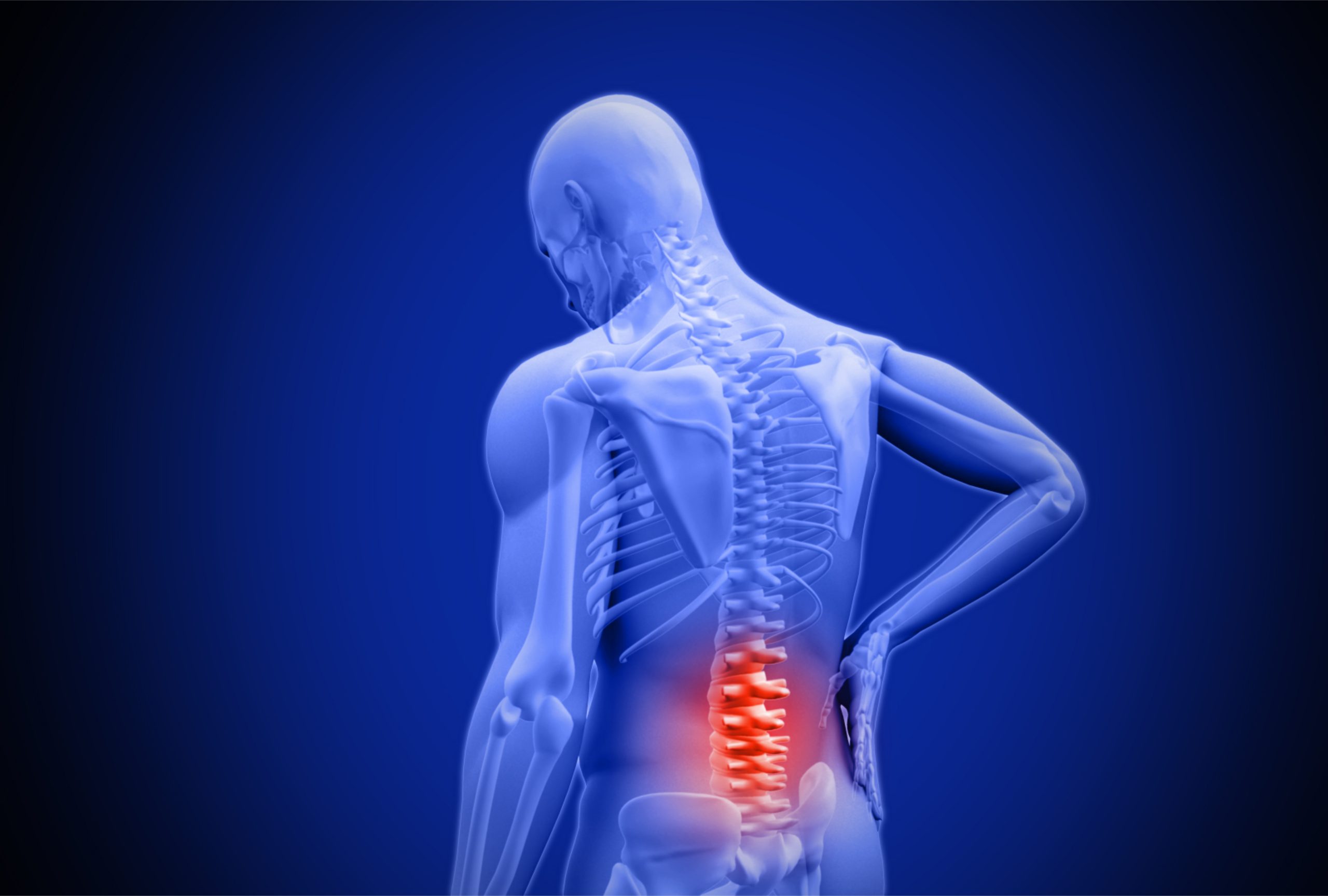
Introduction:
Lower back pain is a prevalent condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is the leading cause of disability and missed workdays. While several factors can cause it, it is most commonly associated with age-related degeneration of the spine, injuries, and lifestyle choices. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for lower back pain.
Causes of Lower Back Pain
Lower back pain can be caused by several factors, including:
Muscle or ligament strain
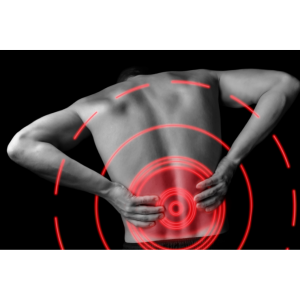
Muscle and ligament strain is a common cause of lower back pain. It occurs when the muscles or ligaments in the back are stretched beyond their normal limits, either due to overuse or injury.
Straining can cause intense pain, stiffness, and limited mobility, making it difficult to perform even simple tasks.
Muscle strains occur when the muscle fibres are torn or stretched beyond their normal capacity, causing damage to the tissue. This type of injury is commonly associated with overuse or sudden movements that cause the muscle to contract too quickly. Ligament strains, on the other hand, occur when the ligaments are stretched beyond their normal range of motion, causing them to become damaged or torn.
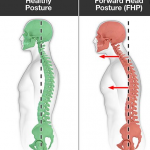
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing muscle or ligament strain in the back. These include poor posture, lack of exercise or physical activity, being overweight or obese, and participating in sports or other activities that require repetitive or strenuous movements. Additionally, people who have a history of back problems, such as a previous injury or condition, are at an increased risk of developing a strain.
Symptoms of muscle or ligament strain can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Mild strains may only cause discomfort and stiffness, while more severe strains can cause intense pain, swelling, and bruising. In some cases, the pain may radiate down into the legs, making it difficult to stand or walk.
Treatment for muscle or ligament strain typically involves rest, ice, and compression. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as panadol or ibuprofen, may also be recommended to help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
Prevention is key when it comes to muscle or ligament strain in the back. Maintaining good posture, engaging in regular exercise and physical activity, and using proper lifting techniques can all help to reduce the risk of developing a strain. Additionally, taking breaks and stretching during long periods of sitting or standing can help to relieve tension in the muscles and prevent strain. 
In conclusion, muscle or ligament strain is a common cause of lower back pain that can be caused by overuse or injury. While treatment options are available, prevention is key to avoiding the discomfort and limited mobility associated with a strain.
Herniated discs
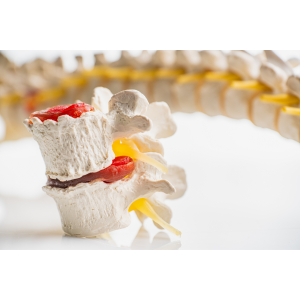
Herniated discs can be a very painful and debilitating condition. It occurs when the soft material inside the discs of the spine leaks out, irritating nearby nerves and causing pain.
This condition can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, making it challenging to carry out even the most basic of daily activities.
The spine consists of 24 vertebrae, and between each of these vertebrae lies a small, rubbery cushion known as an intervertebral disc.
These discs act as shock absorbers, protecting the spine from damage during everyday activities such as walking, bending, and twisting. The discs also help to maintain proper spacing between the vertebrae and allow for the smooth movement of the spine.
However, when a disc becomes herniated, the soft material inside it, called the nucleus pulposus, leaks out through a tear in the tough outer layer of the disc. This leakage can irritate nearby nerves, causing pain, numbness, or weakness in the affected area. Herniated discs can occur in any place places along the spine, but they are most common in the low back and neck.
Several factors can increase the risk of developing a herniated disc, including age, genetics, obesity, and poor posture. Individuals who perform repetitive activities, such as lifting heavy objects, or who sit for extended periods may also be at risk.
Fortunately, many non-surgical treatments can help manage the symptoms of a herniated disc. These treatments may include physical therapy, pain medications, chiropractic care, and exercise. In some cases, a doctor may recommend spinal injections, such as epidural steroid injections, to help reduce inflammation and relieve pain.
For individuals with severe symptoms or who do not respond to non-surgical treatments, surgery may be necessary. Surgery can involve removing the damaged portion of the disc or fusing the affected vertebrae to prevent movement that can further aggravate the herniated disc.
It’s essential to seek medical attention if you suspect that you may have a herniated disc. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent further damage to the spine. A doctor can perform a physical exam, review medical history, and order imaging tests, such as an X-ray or MRI, to confirm a diagnosis.
Spinal stenosis:
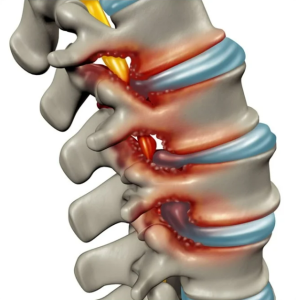 is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the spinal canal, which is the channel that houses the spinal cord and nerves, becomes narrowed. This narrowing can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, leading to a variety of symptoms that can range from mild to severe.
is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the spinal canal, which is the channel that houses the spinal cord and nerves, becomes narrowed. This narrowing can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves, leading to a variety of symptoms that can range from mild to severe.
The spinal canal is normally wide enough to allow the spinal cord and nerves to move freely. However, in some cases, this canal can narrow due to various factors. One of the most common causes of spinal stenosis is age-related degeneration. As we get older, the spinal discs can lose their elasticity and become less effective at cushioning the vertebrae. This can lead to a narrowing of the spinal canal and subsequent pressure on the spinal cord and nerves.
Other causes of spinal stenosis include herniated discs, spinal injuries, tumours, and genetic conditions such as scoliosis. In some cases, spinal stenosis can also be caused by lifestyle factors such as obesity, lack of exercise, and poor posture.
The symptoms of spinal stenosis can vary depending on the location and severity of the narrowing. Common symptoms include pain, numbness, and weakness in the back, legs, and arms. Some people may also experience difficulty walking, loss of balance, and bowel or bladder problems.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention. A doctor can perform a physical exam and imaging tests to diagnose spinal stenosis and develop a treatment plan.
Treatment for spinal stenosis typically involves a combination of non-surgical and surgical approaches. Non-surgical treatments may include physical therapy, pain management, and lifestyle modifications such as weight loss and exercise. In some cases, steroid injections may also be recommended to help reduce inflammation and pain.
Surgery may be necessary if non-surgical treatments are not effective or if the spinal stenosis is severe. The type of surgery recommended will depend on the location and severity of the narrowing. Common surgical procedures for spinal stenosis include laminectomy, which involves removing part of the vertebrae to widen the spinal canal, and spinal fusion, which involves fusing two or more vertebrae to provide stability.
In conclusion, spinal stenosis is a condition that can cause a variety of symptoms and can have a significant impact on your quality of life. If you are experiencing any symptoms of spinal stenosis, it is important to seek medical attention as soon as possible. With the right treatment, many people with spinal stenosis can manage their symptoms and lead a full and active life.
Osteoarthritis:

This degenerative joint disease typically develops as a result of wear and tear on the joints over time, causing the cartilage to break down and bone to rub against bone. The result is pain, stiffness, and swelling in the joints, which can significantly impact one’s quality of life.
One of the most common areas affected by osteoarthritis is the lower back. Many people with this condition experience lower back pain, which can be debilitating and interfere with daily activities.
However, the symptoms of osteoarthritis can manifest in any joint in the body, including the hips, knees, hands, and feet.
While osteoarthritis is more prevalent in older adults, it can occur at any age. Other risk factors for developing osteoarthritis include obesity, joint injuries, and genetics. Women are also more likely to develop osteoarthritis than men.
The symptoms of osteoarthritis can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Some people may only experience mild discomfort, while others may have severe pain and limited mobility. Common symptoms include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and a crunching or grinding sensation when moving the affected joint.
Fortunately, there are many treatment options available for osteoarthritis. In mild cases, lifestyle modifications such as weight loss, exercise, and physical therapy may be enough to manage symptoms. In more severe cases, medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids may be necessary to relieve pain and inflammation.
For people with advanced osteoarthritis, joint replacement surgery may be an option. This procedure involves replacing the damaged joint with an artificial one, which can significantly improve mobility and reduce pain.
It’s important to note that there is no cure for osteoarthritis. However, with proper management and treatment, people with this condition can still lead active and fulfilling lives. If you are experiencing joint pain or other symptoms of osteoarthritis, it’s essential to speak with your doctor to determine the best course of treatment for your individual needs.
In conclusion, osteoarthritis is a common condition that affects the joints and can cause lower back pain. While there is no cure, there are many treatment options available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for osteoarthritis, people with this condition can take an active role in their care and live life to the fullest.
Scoliosis:

Scoliosis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a spinal deformity that causes the spine to curve to the side, leading to lower back pain and other related symptoms. This condition can affect people of all ages, from children to adults, and can range from mild to severe.
The curvature of the spine in scoliosis can occur in different directions, with the most common being a side-to-side curvature that resembles the letter “S” or “C”. While the exact cause of scoliosis is not known, it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some people may be born with scoliosis, while others may develop it later in life due to factors such as poor posture, injury, or a medical condition.
One of the most common symptoms of scoliosis is lower back pain. This pain can be mild to severe and can also be accompanied by stiffness and muscle spasms. As the condition progresses, it can also lead to difficulty breathing, fatigue, and decreased mobility.
While there is no cure for scoliosis, there are several treatment options available to manage the symptoms and prevent the condition from worsening. One of the most common treatments is bracing, which involves wearing a brace that helps to straighten the spine. This is typically used for children and adolescents who are still growing and whose curvature is between 20-40 degrees.
For those with more severe cases of scoliosis, surgery may be required. Spinal fusion surgery involves fusing the affected vertebrae to straighten the spine and prevent further curvature. While this is a more invasive treatment option, it can be effective in reducing pain and preventing further damage to the spine.
In addition to medical treatments, physical therapy treatment can be very effective in reducing the curve and the accompanying spinal rotations. Lifestyle changes can also help to manage the symptoms of scoliosis. This includes maintaining good posture, engaging in regular exercise to strengthen the muscles around the spine, and avoiding activities that may exacerbate the curvature, such as heavy lifting or twisting.
Overall, scoliosis is a complex condition that requires a personalised approach to treatment. If you are experiencing lower back pain or suspect that you may have scoliosis, it is important to consult with a health professional to determine the best course of action for your individual needs. With the right treatment plan and lifestyle changes, it is possible to manage the symptoms of scoliosis and live a healthy, active life.
Symptoms of Lower Back Pain
The symptoms of lower back pain can vary depending on the underlying cause. However, some common symptoms of lower back pain include:
- Pain that radiates down the leg
- Stiffness or decreased range of motion in the back
- Muscle spasms
- Numbness or tingling in the legs or feet
- Pain that worsens with activity
Treatment Options for Lower Back Pain
The treatment options for lower back pain will depend on the underlying cause. However, some common treatment options for lower back pain include:
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles in the back and improve flexibility.
- Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen can help relieve lower back pain.
- Surgery: Surgery may be necessary for severe cases of lower back pain that do not respond to other treatments.
- Chiropractic care: Chiropractic care can help alleviate lower back pain by realigning the spine.
- Electrical Muscle Stimulation (EMS): EMS devices use mild electrical impulses to stimulate muscles, promoting circulation, easing tension, and supporting pain relief.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Can stress cause lower back pain?
A: Yes, stress can cause lower back pain.
Q: When should I see a doctor for lower back pain?
A: You should see a doctor if your lower back pain is severe, does not improve with rest, or is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever or difficulty urinating.
Q: Can exercise help alleviate lower back pain?
A: Yes, exercise can help alleviate lower back pain by strengthening the muscles in the back and improving flexibility.
Conclusion
Lower back pain is a common problem that affects millions of people worldwide. While several factors can cause it, it is most commonly associated with age-related degeneration of the spine, injuries, and lifestyle choices.
If you are experiencing lower back pain, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and the best course of treatment. With the right treatment plan, you can alleviate your lower back pain, improve your quality of life and get back to the things you enjoy back pain-free!